Internet is a major part of our lives in the 21st century, from individuals to industries. There have been many ways to access what the internet has to offer which is done by networking. The common ways computing technology devices connects is either wired or wireless (Hub Bridge, Switches, Routers). Internet is also a computing technology device that can transfer between a host device to another device, or multiple devices at once. The user’s computer or mobile device sends and receives waves to the relevant party on the fixed network or through other base stations connected to the operator’s computer-based central exchange via other base stations.
Data is sent from one network access point and another, or between multiple network access points, using data switching, transmission lines, and system controls. Only a few examples of the communication technologies that make up data networks are circuit switches, leased lines, and packet switching networks. Data is sent between computers over the Internet by being divided into tiny units called “packets” and sent to the other device.
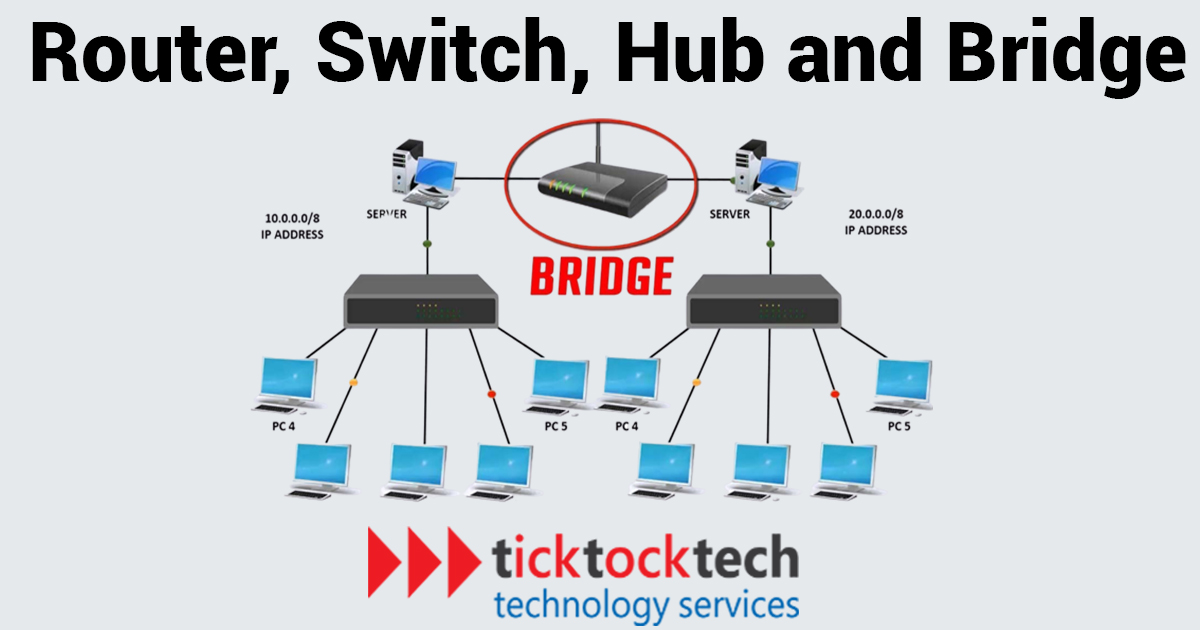
The connection range depends on the type of network used. We have many network types but the most common ones are the Personal Area Network (PAN), Local Area Network (LAN), and the Wireless Local Area Network (WLAN). A local area network (LAN) is a collection of computers and related peripherals that connect wirelessly or through a wired network to a server located within a certain geographical region. A local area network can accommodate two or three users working from home or thousands of users in the industry. Talking about local area network connections, we have the Hub, Bridge, and Switches while the wireless version is Routers.
Routers
Basically, a router sends and receives data over computer networks. By directing data packets to their intended IP addresses and enabling several devices to use a single Internet connection, it manages traffic between these networks. These are among the most popular types of wifi wireless connections. To enhance Internet access or support the creation of commercial networks, routers can connect to these devices and combine the tasks of switches and hubs.
Significant difference
From the definitions, Hub, bridge, switches and routers seem to sound similar but are variably different, especially in how they forward network traffic to the connected devices. A router provides connections between different network architectures. Also, it is smart enough to choose the best path to deliver a network using the dynamic routing algorithm. However, routers are slower because they need to analyze data before sending them to connected devices. Routers are also expensive compared to hubs and switches and offer low bandwidth.
Hubs
A simple networking device that links several local area network (LAN) components together. Every computer or Ethernet-based device linked to a network hub receives data that is broadcast to all of those devices. The hub relays the electrical signals obtained on one port to all other ports that are linked. When several Ethernet devices are connected to one another, they function as a single network segment. Also known as a multiport repeater, network hub, repeater hub, or active hub over Ethernet.
Difference
The Hub is less intelligent as it does not filter data and doesn’t know where data is to be sent. The Hub works by broadcasting or repeating packets to all of its ports (other network devices). A collision occurs when two network devices on the same network try to send packets at the same time. The high tendency of collision makes it less secure for crucial data. Concerning the hub’s inability to filter data, it sends all data received down to its port which leads to wastage of bandwidth and insecurity. However, they are the cheapest out of the four networking devices.
Bridges
A bridge network is a Link Layer device that passes traffic between network segments, in relation to what “bridge” normally signifies. A bridge can be either a hardware component or a kernel-level software component on the host machine. Bridges assist in increasing the network capacity of a single LAN by connecting numerous LANs. They typically function at the data connection layer, sending data in frames. For instance, LAN 1 might be an Ethernet LAN and LAN 2 might be a token ring-style data link.
Significant Difference
The bridge however processes and records information about signal traffic between devices in the networks. It then used the stored information to get the most efficient path for data transfer between the transmitting and receiving device. This is similar to filtering in switches but switches are faster
Switches
As compact devices that may accept data from several input ports and transfer it to a specified output port that sends the data to its intended location in the network, hubs and this are pretty similar. To allow communication between several networked devices, many data cables are inserted into a switch. Multiple devices are connected by a switch to form a sizable network, and other switches and their separate networks are connected by routers to make even bigger networks.
Significant differences
Unlike Routers, A switch only sends data to the single device it is intended for. A switch is more technical as it can identify which device is connected to an exact port. Done by using the MAC address(unique addresses used to identify computers).
With this, it has the ability to deliver the message to a particular machine. Compared to the Hub, switches increase the bandwidth in a network and also lower the chance of frame collision. They are more secure because they deliver data to specific ports or nodes. This means they have the ability to filter data. However, switches are more expensive compared to hub devices.