Have you ever found that your streaming TV is slow or your downloads are slow even though you have high speed internet? Have you ever asked your roommate or a family member, “are you downloading something?” or “what are you playing on PlayStation”? Your internet bandwidth might be used up by a device you’re not aware of.
The other day I was thinking that some of my roommates here at the University of Regina were using up all of the internet bandwidth. At first I took my computer in to a repair shop to make sure it wasn’t my machine (slow internet) and they said everything was fine. I started looking around the internet to find ways to look and see who was using up all the internet and slowing things down. I found some pretty useful stuff.
Here are some tips to help you identify what’s going on with your network.
There usually are several devices connected to your network at one time. Some devices can be using up your bandwidth without you even using them. Sometimes it’s malware or an unwanted intruder.
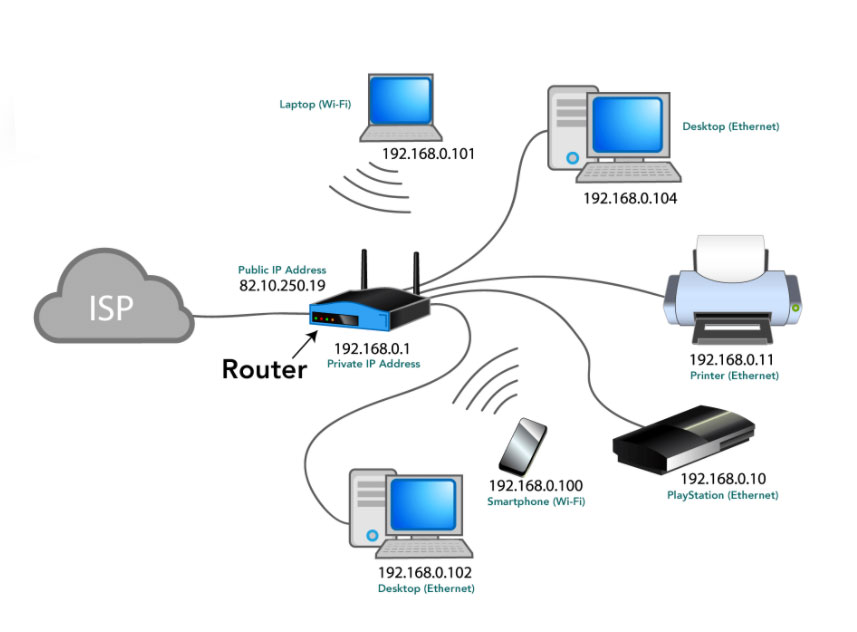
Your Router Can Track Your Internet Bandwidth
If you login into your router you can see a list of all the devices attached to your network. You can check IP addresses, MAC addresses, and see whether they’re connected or not. It will show you how much data each device is currently using and how much download/upload speed you have. Most routers have this capability.
Here is an example of what the router screen looks like, courtesy of makeuseof.com
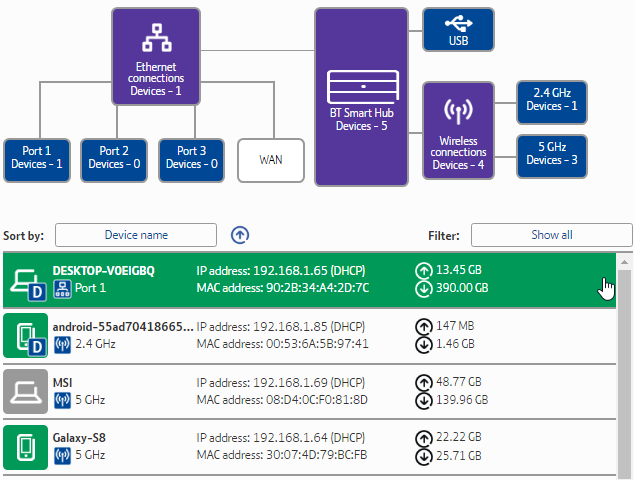
You can remove any of these devices if you do not recognize them, but make sure not to delete the ones you do recognize. You’ll have to re-enter your credentials to connect them again which can sometimes be a major hassle.
Check Bandwidth Usage With Capsa (Free)
Another option to check your bandwidth is using a third-party program. You can use Capsa, a free network analysis program that captures every data packet engaging with your system.
- Select the network adapter for your system. For me, it is Ethernet. For you, it might be a Wi-Fi adapter. Choose Full Analysis, then hit Start to get things underway.
- In the Node Explorer (left-hand side), head to Protocol Explorer > [your adapter type] > IP. The tree of protocols expands, but you can stop here.
- In the analysis panel, select the Protocol The Protocol tab shows data packets for each protocol your system is using.
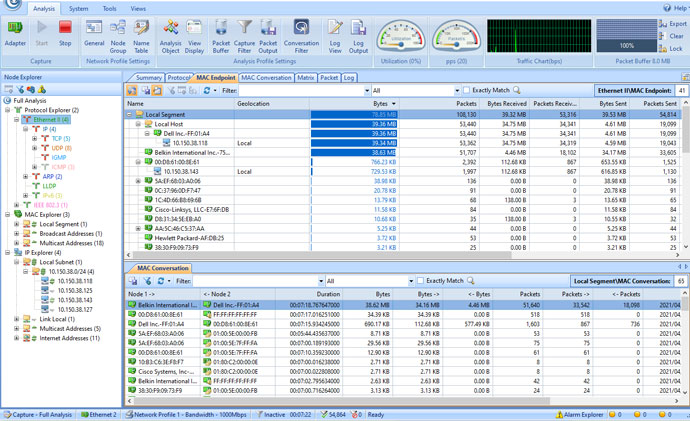
- In the analysis toolbar at the bottom of the screen, select MAC Endpoint. If you double-click your device IP address, it will open the detailed packet analysis screen for you.
Loads of common traffic have easily identifiable addresses. In other places, Capsa marks the traffic for you.
You can re-arrange the way you want to see the information. In the analysis panel, hit the IP Endpoint tab, then browse to your device IP address. The analysis toolbar shows all of the incoming and outgoing connections for the local host, its geographic endpoint, and more.
You can download Capsa for free here.
Malware Can Slow Your Internet Down Significantly
Slow computing, unexpected behaviors, excessive pop-ups and frequent crashes can all be signs of malware. If you are experiencing any of the above symptoms, you may be dealing with a malware infection. Here’s a typical timeline for a malware invasion.
You visit a website, open an email message or download a picture. Somewhere in your normal online computing activities, malware silently loads itself onto your computer. Once on your PC, it sets up shop by installing itself in many places. This makes it difficult to remove and can lead to disruption of all the files and programs to which malware has attached itself.
Malware activity bogs down PC processes. Malware in action can consume a substantial amount of your computer’s memory, leaving limited resources for other legitimate programs to use. This can lead to extremely sluggish performance of vital programs, like your Internet browser or operating system and a slow PC overall.
Files become damaged and programs malfunction. The most noxious malware can cause more than inconvenient disruptions. It can bring your PC crashing down to a grinding halt by:
- Deleting, changing, renaming or transferring files
- Opening and closing programs at will
- Interfering with your operating system, resulting in frequent PC crashing
You can no longer rely on your PC to operate properly, if at all. With all these malware symptoms wreaking havoc on your PC, you can never count on programs to run properly or files to remain intact. Eventually, you may not even be able to open programs or start your computer at all.
Use Netstat to Show Network Information
Another way to hone in on system processes hogging your bandwidth is through the Command Prompt and the netstat command. Netstat is short for “network statistics,” and you can use the command to evaluate all the network comings and goings on your system (but not your router).
In your Start menu search bar, type command, then right-click and select Run as Administrator. When the Command Prompt opens, input netstat -o and press Enter. What follows is a long list of every active network connection on your computer, which port they’re listening on, the external address, and which process the network connection belongs to.
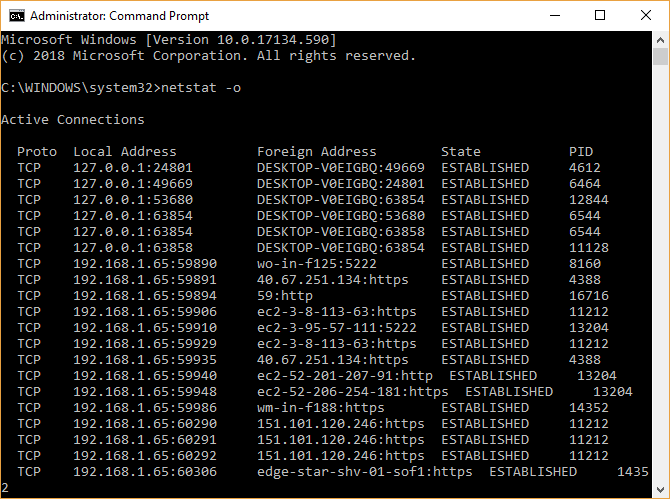
Scan through the list and see if there are any unusual entries. You can copy and paste an address into your browser to search for it. The vast majority of entries are for servers or cloud servers of one kind or another because they’re the backbone of the internet.
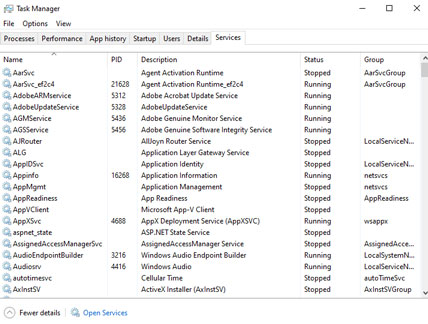
You can also note the PID (Process ID). Open your Task Manager, then the Services tab, and locate the equivalent process. If the PID has a lot of open network connections in the Command Prompt, and it is a service you don’t recognize, you can either stop the service and see if it clears your bandwidth issues, or complete an internet search to figure out what the process is and if it’s something your system requires.
Windows Performance Monitor
There is a more advanced way to see what taking up your bandwidth. It’s the Windows Performance Monitor. This is more advanced but this blog is very thorough in explaining how it works: How to Use the Windows Performance Monitor
While you’re in the Task Manager, to get to another internet bandwidth troubleshooting tool, click on the Performance tab, and then click on the “Resource Monitor” button at the bottom.
A glance at the Send and Receive columns shows me that Chrome and Malwarebytes currently account for most of my bandwidth. Seeing Chrome and Malwarebytes at the top of the list is fine because I trust both of these programs. If you see an unknown process or application at the top of the list, draining your bandwidth, it is time to start investigating.
The resource monitor is super powerful, but it is very advanced.
What’s Using Your Internet Bandwidth?
It is a good question. In my house there can be up to ten devices competing for bandwidth at times.
Not that I suggest cutting your family or friends bandwidth off. However, if you have a persistent bandwidth drain and you’re sure it isn’t a device within your control, one of the above tips on monitoring your home network use will uncover the perpetrator.
Here is a helpful video
Check out more of our blog posts here.