Have you ever wondered how some websites load quickly, while others take forever to load? The secret to their speed lies in a technology called Content Delivery Network (CDN). But what exactly is a CDN, and how does it work?
What is a Content Delivery Network (CDN)?
In simple terms, a CDN is a network of servers located across different geographic locations. When you request to load a web page, the CDN directs your request to the server closest to your location. It stores a copy of the website’s content on multiple servers spread out across the globe. This way, when you visit a website, your request goes to the closest server, not to the original server. This short trip makes websites load faster, making your online experience smoother.

CDNs play a crucial role in the smooth functioning of the internet. Whether you’re aware of it or not, CDNs influence almost every aspect of your online experience. From browsing news articles to shopping online, streaming movies, or scrolling through social media, CDNs are there, ensuring that content loads efficiently on your device.
Why is a Content Delivery Network (CDN) important?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) plays a crucial role in speeding up the internet. When you visit a website, your request travels a long way to reach the server where the website lives. This distance can slow things down, causing delays or latency.
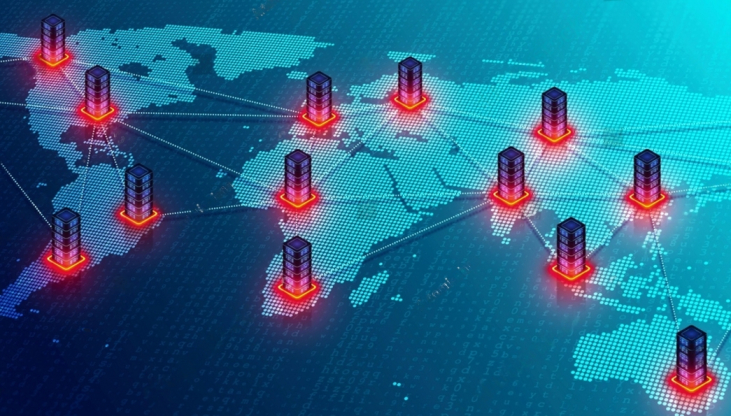

Latency is a common issue that CDNs address. It’s the frustrating delay between requesting a webpage and the content appearing on your screen. This delay can be caused by different factors, including the physical distance between you and the website’s hosting server. The farther away a website’s hosting server is from your location, the longer it takes for the content to load. By using a CDN, websites can virtually shorten that distance, making their content appear on your screen faster.
What are the Benefits of CDNs?
Using a Content Delivery Network (CDN) offers several benefits for better website performance. Here are some of the benefits of using a CDN:
- Faster Page Loading: CDNs reduce the distance between your website’s hosting server and your users. This means your website’s content is delivered faster.
- Improved User Experience: Faster page loading times mean a better user experience. Your visitors will be more likely to stay on your website, engage with your content, and even come back for more.
- Enhanced Security: CDNs often have built-in security features, like DDoS protection and SSL encryption. This means CDNs also protect websites against cyber-attacks and data breaches.
- Increased Conversion Rates: A faster website means higher conversion rates. When your website loads quickly, visitors are more likely to sign up for a newsletter, make purchases, or take any other desired action.
In addition to these use cases, CDNs offer benefits such as multi-user scaling, real-time streaming, and improved user experience. They have become integral to many business models, including SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS, and are widely utilized across diverse sectors to provide a seamless web experience.
How does a CDN work?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) uses three main types of servers to speed up the internet for you:
- Origin Servers: These are the main servers where the original content is stored. Think of them as the main library for storing information. If something needs to be updated, it’s done here. These servers can either be managed by the website owner or hosted on big cloud platforms like Amazon AWS or Google Cloud.
- Edge Servers: These servers are like local branches of the main library, spread across different places around the world. They store copies (caches) of the content from the origin server. When you want to see something online, you get it from the nearest edge server, not directly from the origin server. This makes things faster. If the info on the edge server is old, it gets the new info from the origin server.
- DNS Servers: These servers act like the internet’s address book. They help your computer find where the content is stored, pointing you to the closest edge server so you can get the content quickly.
How does a CDN make your Internet Fast?
If you’re in New York and want to visit a website based in London, it could be slow because the data has to travel a long way. A CDN fixes this by keeping a copy of the website’s content in different locations worldwide. So, instead of fetching the website from London, you get it from a location close to New York. This reduces the time it takes for the website to load.
CDNs do two main things:
- Reduce Latency: Latency is the delay before a transfer of data begins following an instruction for its transfer. CDNs minimize this delay by making sure the data doesn’t have to travel too far to reach you. The closer the data is, the quicker you can access it.
- Balance Loads: Just like spreading out traffic on roads to avoid jams, CDNs manage internet traffic to prevent overload on any one server. This means even if lots of people are trying to access the same content, the CDN can handle it smoothly, ensuring everyone gets a fast and reliable experience online.
Frequently Asked Questions
Conclusion: How does a Content Delivery Network (CDN) work?
A Content Delivery Network (CDN) is an essential tool for enhancing online experiences by speeding up content delivery. It does this through a network of servers to ensure everyone can access web content quickly. By reducing latency and balancing loads, CDNs improve website performance, security, and user satisfaction. Whether you’re streaming or shopping online, CDNs work silently in the background to make your internet faster and more reliable.