Ever wondered what powers the digital world, allowing you to access your data and applications anytime, anywhere? The answer lies in Server-Based Computing (SBC). This technology is the backbone of modern digital services, from streaming your favorite shows to accessing work documents remotely. But what exactly is server-based computing, and how does it impact businesses? Let’s dive in.
What is Server-Based Computing?
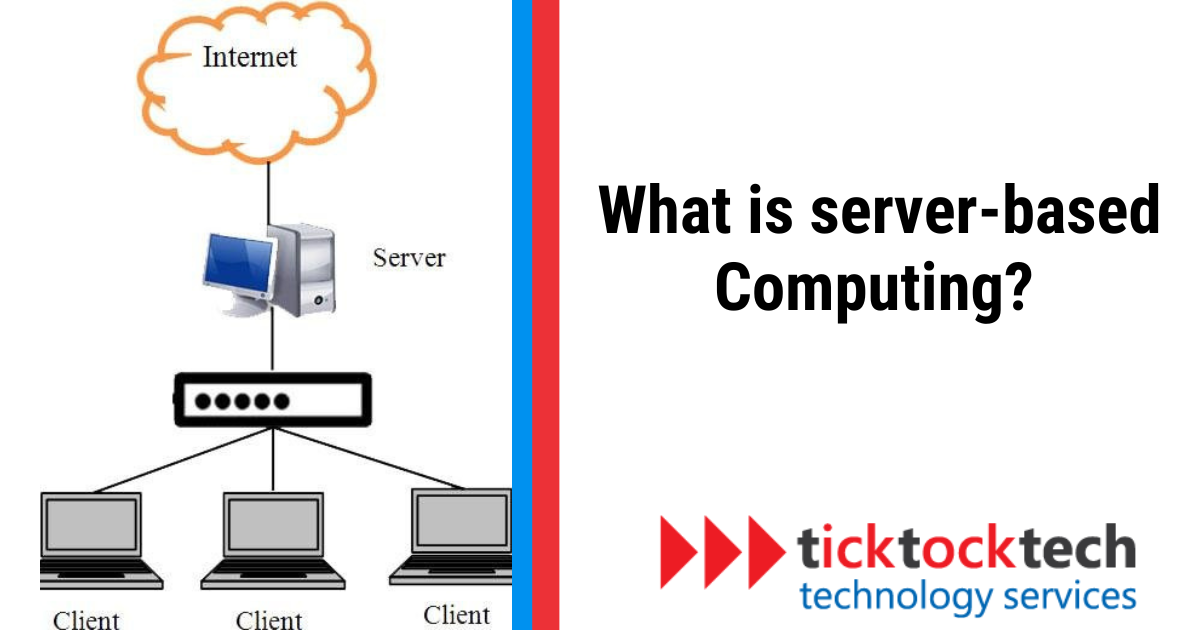
Server-based computing (SBC) is a technology framework that operates, manages, and supports applications entirely from centralized server farms. In this setup, the interaction with the applications, through screen displays and input from keyboard and mouse, occurs over a network between the server farms and the client’s device. Unlike traditional computing models, in SBC, the applications do not run locally on the user’s desktop or device.
SBC provides seamless and immediate access to essential business applications and data from a centralized location. This approach streamlines management and enhances security since all application activities are within the server environment.

Echoing the operational dynamics of legacy computing systems, such as mainframes and mini-computers (for instance, VAX, AS400), SBC utilizes a modern take on the concept of “dumb terminals.” Historically, these devices did not process data independently but accessed applications running on a central computer system. Similarly, in SBC, the client device primarily serves as an interface, with the heavy lifting done by servers.
This model facilitates efficient application deployment and centralized control, making it a good solution for businesses aiming for streamlined operations and secure data access.
How does it work?
Server-based computing is a computing model that utilizes three essential components to deliver access to applications and data. The first component is a multi-user operating system that enables multiple users to log on and run applications in separate, protected sessions on a single server. This is achieved through Microsoft Windows 2000 Server and Linux variants.
The second component is an advanced computing technology that separates an application’s logic from its user interface. This separation allows only keystrokes, mouse clicks, and screen updates to be transmitted across the network, resulting in bandwidth independence and improved application performance.
The third component is centralized application and client management, which is essential for large computing environments. This component enables organizations to overcome the challenges of managing, accessing, and securing applications. Under the server-based computing model, applications are managed and executed entirely on a server. This centralized approach guarantees secure access to virtually any application across any network.
What are the key business benefits of Server-Based Computing?
Why are companies big and small turning to server-based computing? The benefits are clear and compelling.
- Easy Scalability: SBC allows for the effortless addition of new servers to accommodate growing business needs. This scalability ensures that expanding operations is smooth and interruption-free.
- Increased Security: Direct server logins eliminate the necessity for external storage devices like floppy disks, cutting down the risk of virus infections, data theft, and unauthorized application use. This centralized approach significantly bolsters data security.
- Improved Availability: Solutions provided by leaders in SBC technology, including Citrix, Microsoft, and Tarantella, feature fault tolerance and load balancing. These functionalities enhance the reliability and availability of enterprise systems, ensuring continuous operation and access.
- Lowering Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): SBC enhances manageability and slashes the costs associated with owning applications by up to 50%. By centralizing operations, businesses save on both administrative and hardware costs.
- Boosting Return on Investment (ROI): Investing in SBC can lead to substantial returns. This comes from the reduced need for intensive maintenance and the ability to extend the lifecycle of existing hardware.
- Improved Availability: Solutions provided by leaders in SBC technology, including Citrix, Microsoft, and Tarantella, feature fault tolerance and load balancing. These functionalities enhance the reliability and availability of enterprise systems, ensuring continuous operation and access.
Conclusion
Corporate IT leaders have chosen Server-Based Computing as the top choice for managing applications. It tackles the challenges of making applications more accessible, enhancing performance, and securing data, all while noticeably lowering operational expenses. This model stands out for its efficiency, adaptability, and cost savings, making it a key solution in modern IT strategies.