Space exploration and astronomy are cool, even if you have to go to space (not so many people have anyway.) Telescopes make it easy to view the planetary body from Earth. The farther space however requires a much better and graphical telescope. James Webb space telescopes are the best in this aspect and are used by NASA to view and document far-away planetary bodies. The James Webb Space Telescope is not just a telescope, it’s a big space-like telescope with its own satellite and transmission devices with dynamic positions in space.
The James Webb Telescopes have successfully been used to take some record-breaking clear images and better view of space which includes
Top 8 Accomplishments of the James Webb Space Telescope Mission So Far.
1. Re-imaging the Phantom Galaxy
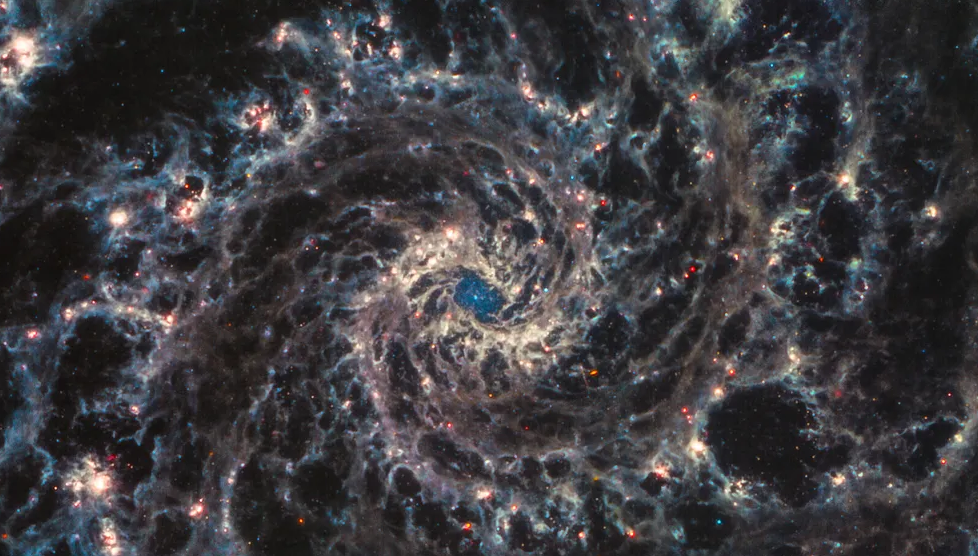

The James Webb Space Telescope has provided a new infrared view of the Phantom Galaxy. This image uncovers intricate, fiber-like structures of dust and gas that are invisible in the optical spectrum. Webb’s advanced infrared capabilities allow astronomers to study the galaxy’s star-forming regions in greater detail, enhancing our understanding of galaxy formation and evolution.
2. Discovery of an Exoplanet
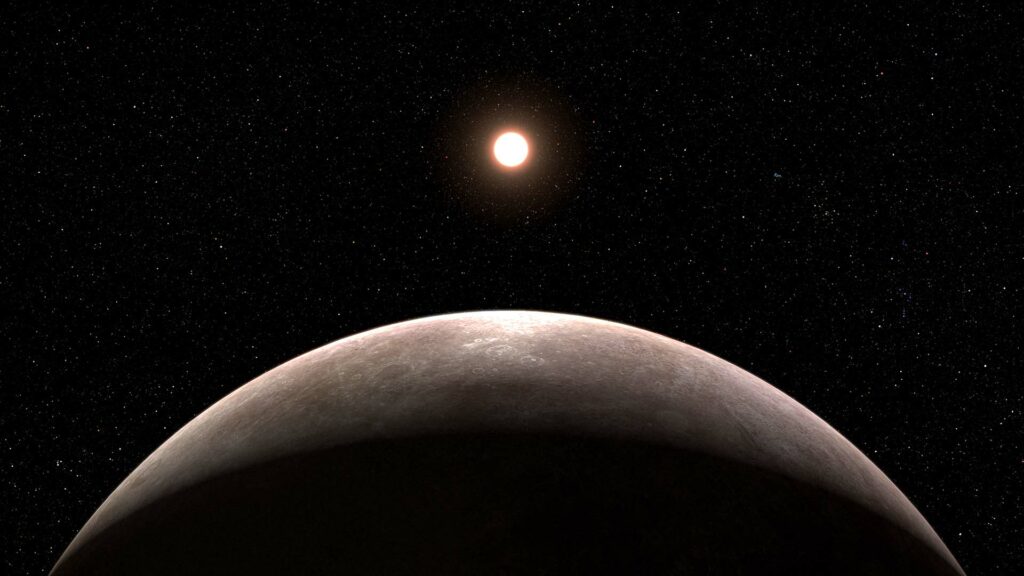

Webb’s first significant exoplanet discovery, LHS 475 b, marks a milestone in space exploration. This Earth-sized planet was identified using Webb’s Near-Infrared Spectrograph, which allowed scientists to analyze its atmosphere. This tool enables a detailed study of exoplanet atmospheres, providing insights into their composition and conditions, which are crucial for understanding their potential habitability.
More in Space: Space Race 2.0: Colonizing Mars and Beyond
3. Clear Image of the Tarantula Nebula

A stunning image of the Tarantula Nebula, revealing young stars that were previously obscured. This nebula is a valuable laboratory for studying star formation because its composition resembles that of the early universe. The image provides unprecedented clarity, helping astronomers study the processes that were common when the universe was at its “cosmic noon.”
4. Discovery of the Farthest Galaxy Ever
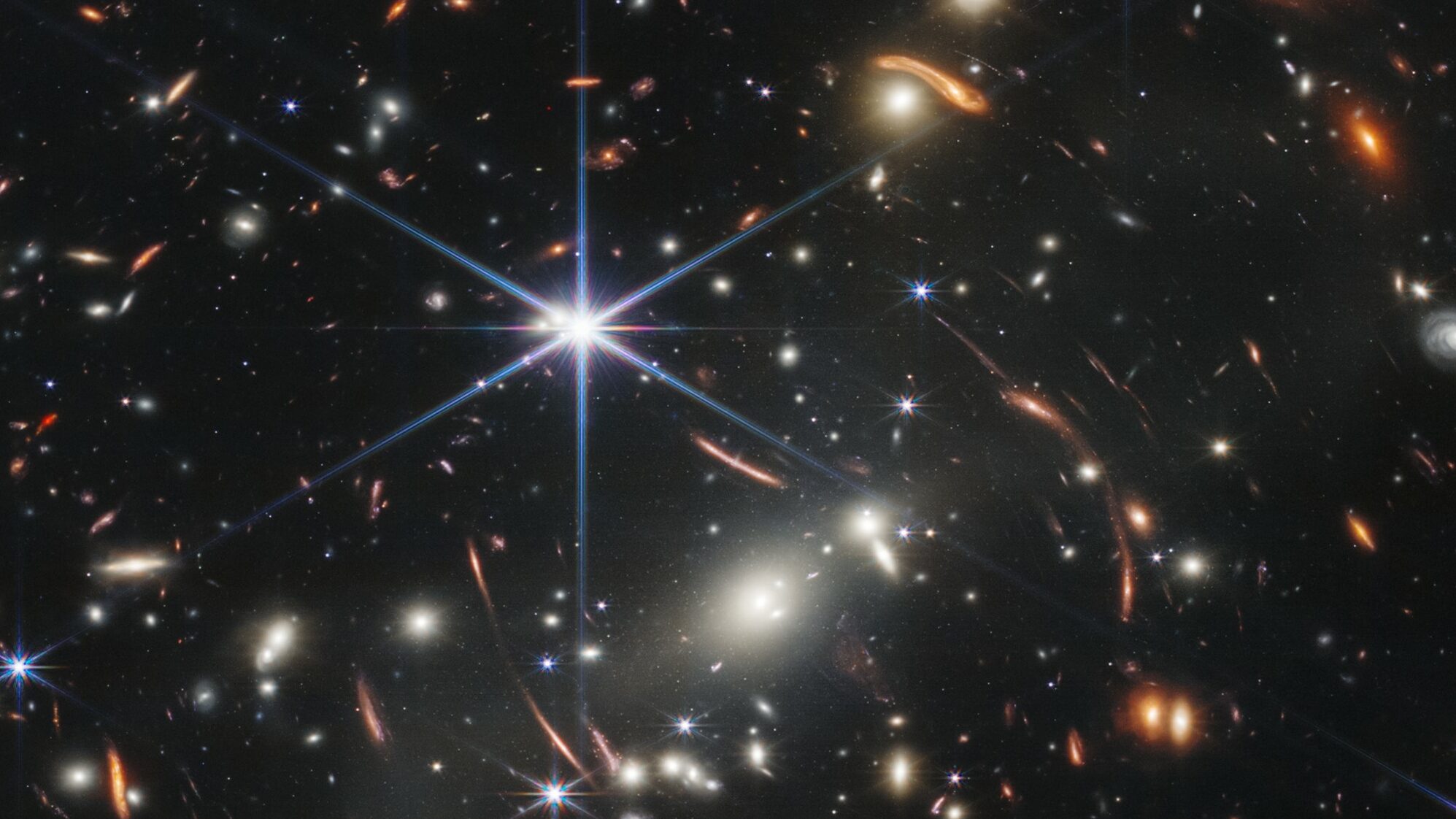

The space telescope pushed the limits of cosmic exploration by identifying some of the most distant galaxies ever observed. These galaxies appear as they did just 350 million years after the Big Bang, offering a glimpse into the early universe. This observation helps scientists understand how galaxies formed and evolved shortly after the universe’s inception.
5. Clearest Ever View of Neptune

Detailed observations of Neptune have revealed the planet’s rings and several faint, previously unobserved bands of dust. These images are the clearest since the Voyager 2 spacecraft flew by Neptune in 1989, providing valuable data on the composition and dynamics of Neptune’s rings and atmosphere.
See Also: SpaceX Starship Launch and the Future of Space Exploration
6. Closer Look into Titan Clouds
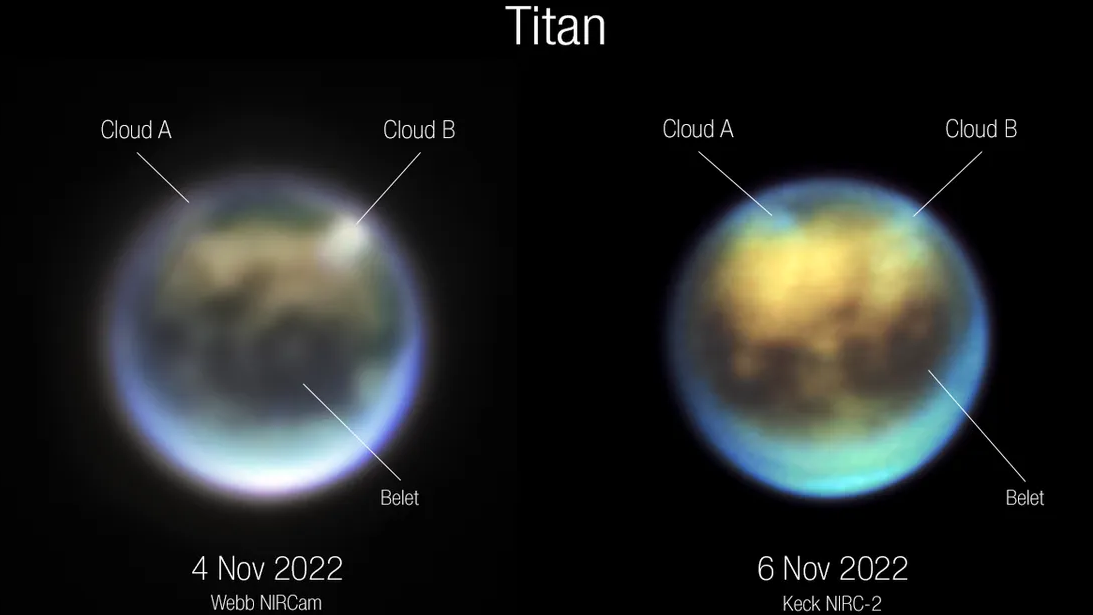

Webb’s observations have provided a new look at Titan, Saturn’s largest moon. The data revealed methane clouds over Kraken Mare, Titan’s largest sea. This observation is key for understanding Titan’s meteorological and hydrological cycles, which are intriguing due to their similarities to Earth’s.
7. Clearest Image of Pillars of Creation

The iconic Pillars of Creation, located in the Eagle Nebula, were imaged by Webb with unprecedented clarity. These new images revealed hundreds of stars that were not visible before and provided detailed insights into how stars are formed from dense clouds of gas and dust.
8. Stunning Image of the Wolf-Rayet Star
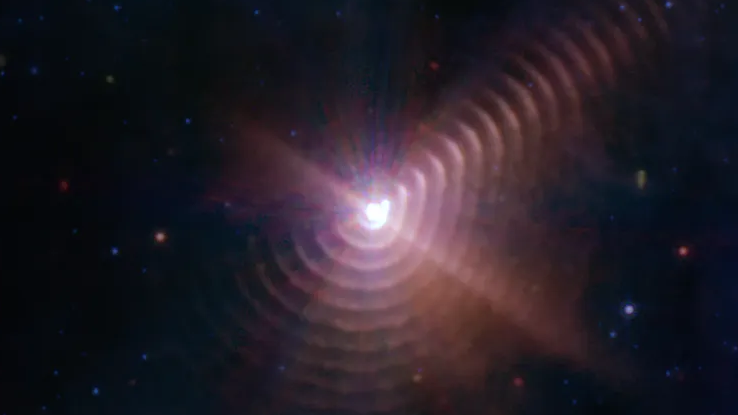

The James Webb Space Telescope captured a spectacular image of the Wolf-Rayet star WR140, showing detailed structures created by the interaction between the star and its companion. These observations help astronomers understand the life cycle of stars, particularly the processes occurring in the late stages of stellar evolution.
Understanding the James Webb Space Telescopes
The James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) is a space observatory aimed at better understanding the universe’s origins. Unlike the Hubble Space Telescope, which orbits the Earth, Webb orbits the Sun, 1.5 million kilometers away at the second Lagrange point.
This position allows it to remain aligned with the Earth as it orbits the Sun, providing a stable viewing platform. The telescope, named after James E. Webb, the NASA administrator during the Mercury, Gemini, and Apollo programs
It is expected to advance our understanding of space and provide unprecedented insights into the universe.
Launched on December 25, 2021, Webb is primarily focused on infrared astronomy. This capability enables it to observe distant galaxies, star formation, and the atmospheres of exoplanets, some of which may be capable of supporting life.
Its sophisticated instruments offer higher resolution and sensitivity than Hubble, allowing astronomers to study phenomena that were previously beyond our reach.
Webb’s mission is expected to last between 5 to 10 years. Which will explore four main scientific themes.
The themes are the universe’s early history, the assembly of galaxies, the birth of stars and planetary systems, and the physical properties of solar systems, including our own.
NASA led the development of the James Webb Space Telescope, in collaboration with the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Canadian Space Agency (CSA).
Features of the James Webb Space Telescopes
Here are the 8 features of the James Webb Space Telescope that produce stunning space images and explorations.
1. Location in Orbit
The JWST operates from a point in space known as the Sun-Earth L2 Lagrange point. This is about 1.5 million kilometers (930,000 miles) from Earth. This position allows it to remain stable relative to the Earth and Sun, providing a constant environment for observation. Its orbit keeps it out of the shadows of both Earth and the Moon, ensuring uninterrupted solar power and constant communication with Earth.
2. Optics Feature
Webb’s primary mirror is a large, 6.5-meter diameter reflector made of gold-coated beryllium. This mirror is segmented into 18 hexagonal pieces, which can be individually adjusted. The large size and specific design of the mirror allow it to gather more light from faint and distant objects in the universe, enhancing its observational capabilities.
3. Operating Software
Webb uses sophisticated flight software that handles data management, spacecraft control, and operation of its scientific instruments. This software is written in a customized version of JavaScript, which allows modular operation where scripts can call on other scripts defined as functions.
4. Component Designs
The JWST features state-of-the-art components that are specifically designed for the harsh environment of space. These include its optical instruments, sun shield, and spacecraft bus—all engineered for precision and durability.
5. Sunshield Protections
The telescope’s sunshield is crucial for its ability to make infrared observations. It consists of five layers made of Kapton material, each as thin as a human hair, coated with aluminum and doped silicon to reflect the Sun’s heat. The sunshield helps maintain the instruments below 50 K (−223 °C; −370 °F), which is essential for infrared observations.
6. Camera Features
The JWST is equipped with several high-performance scientific instruments, including the Near Infrared Camera (NIRCam), Mid-Infrared Instrument (MIRI), and others. These instruments are capable of capturing high-resolution images and spectra across a broad range of infrared wavelengths.
7. Infrared and Sensors
Webb’s sensors are highly sensitive to infrared light, which allows it to observe the thermal signatures of celestial objects and phenomena in the universe. This capability is critical for studying distant galaxies, star formation, and the atmospheres of exoplanets.
8. Repairing Features
While the JWST is not designed to be serviced in space like the Hubble Space Telescope was, it includes several features that could potentially facilitate future servicing missions. These include precise guidance markers on its surface, refillable fuel tanks, removable heat protectors, and accessible attachment points.
Key Components of the James Webb Space Telescopes Spacecraft
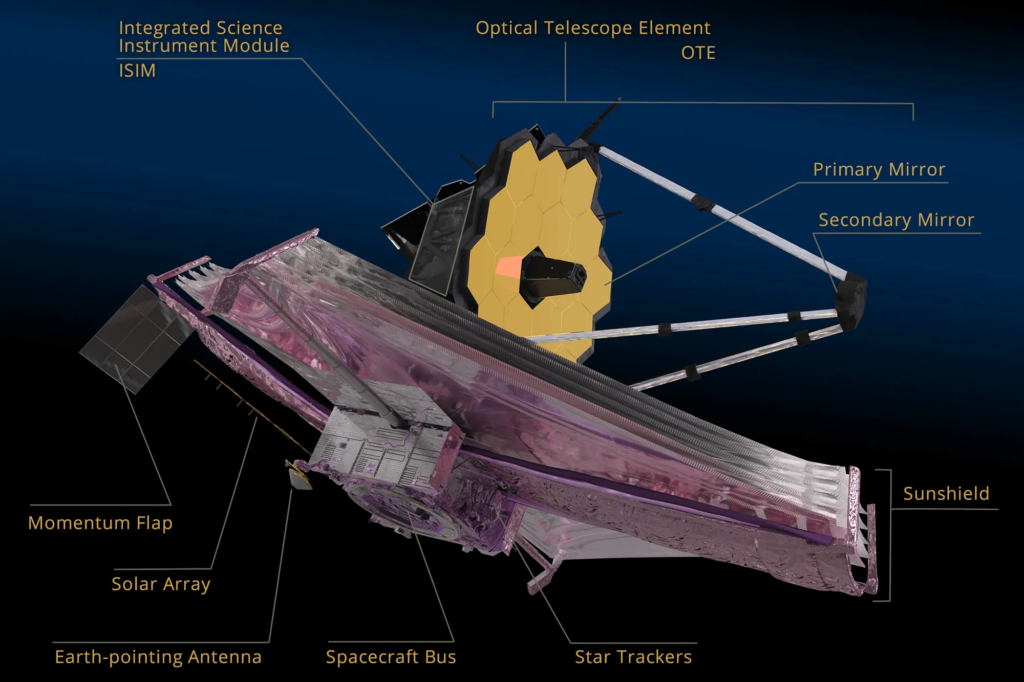
4 key components make the Webb space telescope go on with its mission far inside space. They are Optical Telescope Element OTE, the ISIM and Instruments, The sunshield, and The Spacecraft Bus.
Optical Telescope Element OTE
The Optical Telescope Element (OTE) serves as the observatory’s primary visual apparatus, capturing light from outer space with its mirrors and channeling it to the scientific instruments housed in the Integrated Science Instrument Module (ISIM). The backplane, acting as the observatory’s backbone, provides crucial support for the mirrors, ensuring stability and precision.
ISIM and Instruments
The ISIM is the core unit where Webb’s cameras and scientific tools are integrated. It houses four key instruments, amalgamating numerous subsystems into a single, consolidated payload. This integration is crucial for the telescope’s ability to conduct a wide range of astronomical observations.
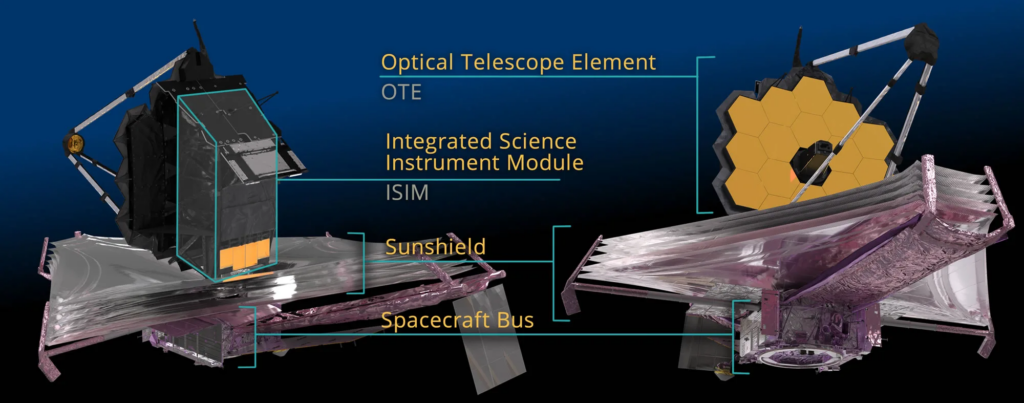
The Sun Shield
This plays a vital role in its operation, dividing the observatory into a hot, sun-facing side (where the spacecraft bus is located.) Also, a cold, shadowed side (home to the OTE and ISIM). This innovative shield is designed to maintain the instruments at a very low operating temperature. The temperature could be —below 50 K (-370°F. This is to ensure optimal infrared sensitivity by blocking out the heat from the Sun, Earth, and the spacecraft’s electronics.
The Spacecraft Bus
Lastly, the spacecraft bus supports the overall functioning of the observatory. It accommodates essential subsystems such as Electrical Power, Attitude Control, and Communication. Also, Command and Data Handling, Propulsion, and Thermal Control. These subsystems are fundamental for Webb’s day-to-day operations. Ensuring it remains powered, oriented, connected, and at the correct operating temperatures.
Conclusions
The James Webb Space Telescope has delivered spectacular achievements since its launch, transforming our understanding of the universe. It has revealed new details in the Phantom Galaxy, discovered the Earth-sized exoplanet LHS 475 b, and provided unprecedented views of the Tarantula Nebula, showcasing young stars.
Additionally, it has observed the most distant galaxies ever seen, offered a clear view of Neptune’s rings, detailed atmospheric features on Titan, captured the intricate Pillars of Creation, and photographed the dramatic effects around the Wolf-Rayet star WR140. These milestones not only underscore Webb’s advanced capabilities but also enhance our cosmic knowledge significantly.
Frequently Asked Questions
The James Webb Space Telescope is special because it operates primarily in the infrared spectrum. This allows it to observe objects in the universe that are too old, distant, or faint for other telescopes like the Hubble.
The James Webb Space Telescope differs from others primarily in its ability to capture high-resolution images in the infrared spectrum.
One of the greatest scientific breakthroughs in 2022 was the James Webb Space Telescope’s detailed observation of distant galaxies as they appeared about 350 million years after the Big Bang.

