Troubleshooting computer problems is one of the most common DIY solutions for users who are familiar with their computers. These solutions can be used mostly in solving software problems. Though there are some hardware problems you can troubleshoot from software like drivers. However, most of the time, this process does not involve dismantling. On Windows 10, you can troubleshoot some problems from the startup or the boot menu.
On this safe reboot page which you can access by pressing the F8 key before the Windows starts while turning on. This will bring different options and one of them is troubleshooting. From this end, you can make some advanced resets or safe reboots to troubleshoot specific computer problems. Now, let’s see what step-by-step process on how to troubleshoot from boot, what problem you can troubleshoot from here, and what to do if it does not work
#1 Restart your Computer
Restart your computer to get started. Hold down the power button until it turns off if it isn’t responding, then turn it back on.
#2 Access the Boot Menu
Keep an eye on the screen as the system wakes up. Typically, a motherboard logo or a manufacturer’s logo (such as Dell, HP, Lenovo, etc.) will be visible. At this early stage, a notification such as “Press [Key] to Enter Setup” or “Press [Key] for Boot Menu” will typically show. Depending on the manufacturer, a specific key may be required to access these options, although it is typically one of the following: F2, F12, Esc, Delete, or Enter. As soon as you see this message, quickly press the appropriate key.

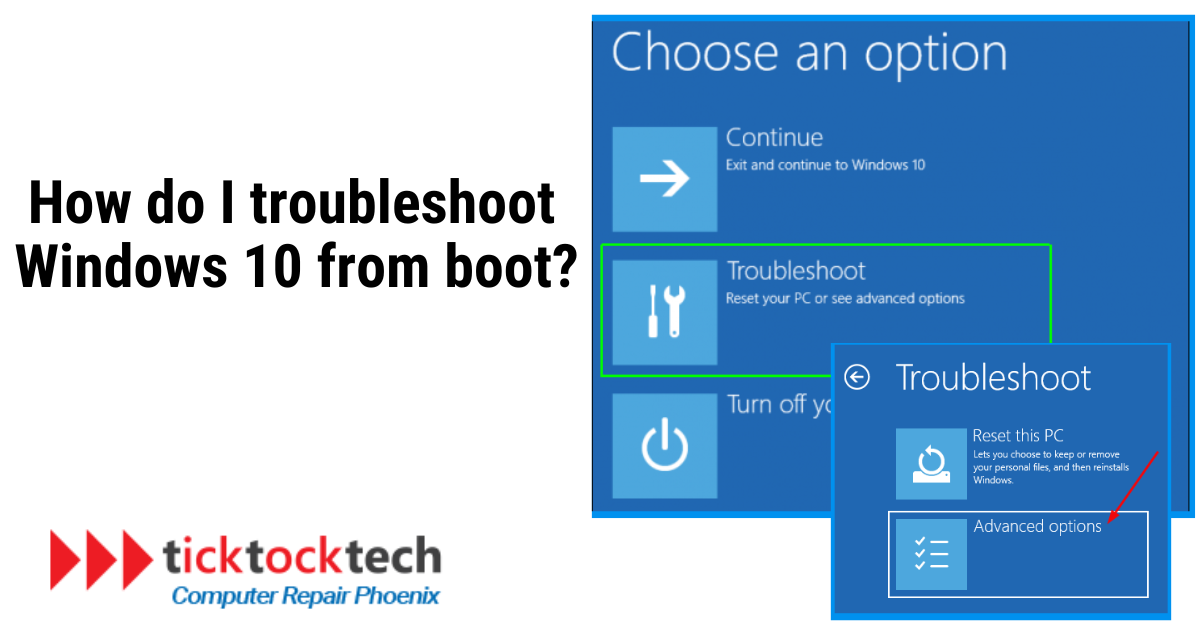
#3 Select Troubleshooting Options from the menu.
Once you’ve reached the boot menu or setup, use the arrow keys on your keyboard to move through the available options. Look for a section on diagnostics, system recovery, or troubleshooting. Depending on the brand and type of your computer, this section’s precise wording and placement can be different.
#4 Select Troubleshoot or Advanced Options
Find the advanced recovery or troubleshooting option under the troubleshooting heading. It might have the headings “Troubleshoot” or “Advanced Options.”
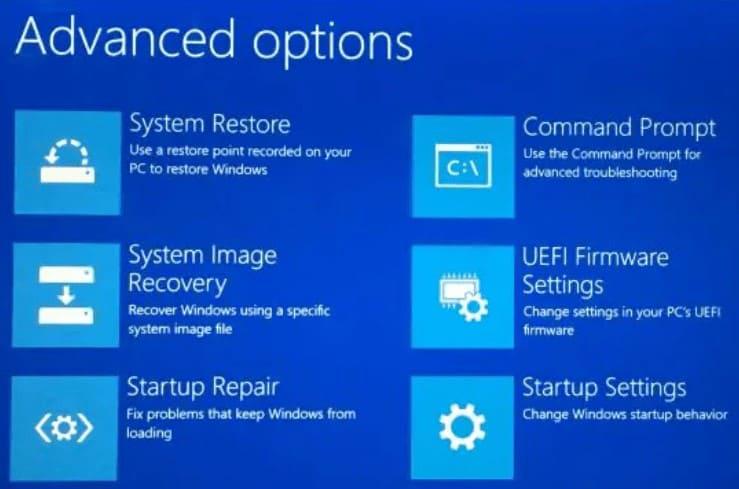
#5 Pick the Necessary Troubleshooting Tool
Depending on your issue, you’ll find different troubleshooting tools or options. Common choices include:
Startup Repair: This tool attempts to automatically fix problems that prevent Windows from starting.
System Restore: You can use this to revert your computer’s system files and settings to an earlier point in time.
Command Prompt: This allows you to manually run various diagnostic commands or execute system repairs.
Boot into Safe Mode: Safe Mode allows you to boot your computer with a minimal set of drivers and services, which can help diagnose problems.
Reset This PC: If your issue is severe, you can choose to reset your PC, keeping or removing your files.
#6 Follow the instructions on the screen.
Use your chosen troubleshooting tool and then adhere to the on-screen directions. The troubleshooting process will be facilitated by these instructions. Before moving forward, make sure you have read and comprehended each step.
#7 Restart your System
Restart your computer to check if the problem has been repaired after you’ve finished the troubleshooting procedure and performed any repairs that were required.
Common Windows 10 Problems you can Troubleshoot from boot
There are different problems on Windows 10 laptops that can be fixed by troubleshooting. This includes some that require troubleshooting from the start. Some of the common ones that can be troubleshooted from boots include the laptop not turning on, booting error, (Blue Screen of Death) BSOD, System Reset, Virus attacks, and Safe mode.
1. Laptop won’t power on:
Start by looking at the power source, such as the battery and charger, if your laptop won’t come on. You might want to conduct a hard reset if they are not the problem. To accomplish this, turn off the laptop, unplug it, take out the battery (if feasible), hold down the power button for about 15 seconds, then put everything back together and try to turn it back on.
2. Boot up error
Frequently, boot issues can be fixed by using Windows’ built-in capabilities. You can enter “Advanced Startup Options” by repeatedly pressing a particular key (often F8 or Shift+F8) while the computer is starting up. Next, select “Troubleshoot” and then “Advanced Options.” After that, you can access choices like “Startup Repair” or “Startup Settings” to address boot-related problems.
Related: How to Fix a Computer that won’t turn on in 2023
3. The Blue Screen of Death (BSOD)
A recently installed driver or piece of software may be to blame for any BSODs you experience. You can enter “Safe Mode” by stopping the boot process several times by repeatedly holding down the power button until the “Automatic Repair” screen appears. Pick “Advanced Options” next, followed by “Startup Settings” and “Safe Mode.” You can delete troublesome drivers or software once you’re in Safe Mode.
4. Viral Attacks
Utilize Windows Defender Offline if you can’t access Windows due to an infection on your PC. Using Windows Defender Offline, make a bootable USB drive, and start your computer from that drive to accomplish this. Next, Windows Defender Offline will check your computer for malware and eliminate it.
5. The safe mode
When debugging different problems, Safe Mode is a useful tool. As previously indicated, the “Advanced Startup Options” menu contains a Safe Mode entry. Working in a steady, uncomplicated environment while in Safe Mode allows you to locate and fix issues with drivers, program conflicts, or viruses.
6. System Reset
You might need to execute a reset if your computer is having serious problems. Select “Troubleshoot” > “Reset this PC” from the “Advanced Startup Options” to carry out this action. To reset your system and keep or remove your files as necessary, simply follow the on-screen directions.
What to do when troubleshooting from boot does not work
Several advanced techniques can assist in resolving enduring computer issues when typical boot troubleshooting approaches are insufficient. If you’ve created restore points, try a system restore. Consider performing a repair install, which involves reinstalling Windows over the present installation to fix more serious problems. As a final resort, make a backup of your data and install Windows Fresh.
Related: Step-by-step process to troubleshoot hardware problems
Starting over and wiping the slate clean, frequently fixes complex issues. Run the built-in hardware diagnostics, which are available during boot through specified keys (such as F12 or F2). Find and repair any broken hardware parts. If you’re unfamiliar with advanced troubleshooting, ask a computer expert or the manufacturer’s support for assistance. These strategies include hardware, software, and expert help to solve complex problems.
Frequently Asked Questions
Troubleshooting Windows 10 from boot involves diagnosing and resolving issues that prevent your computer from starting correctly. It’s often done when a standard startup fails.
Common issues include a laptop not turning on, booting errors, BSOD, system reset problems, virus attacks, and the need to enter Safe Mode.
Depending on your computer’s manufacturer, you can access hardware diagnostics by pressing a specific key (e.g., F12). It helps identify and address hardware-related issues.
Recap
Troubleshooting Windows 10 from boot is a vital skill for resolving software-related issues and maintaining a smoothly operating computer. This step-by-step guide empowers users to access advanced startup options, choose the right troubleshooting tools, and resolve common problems like startup errors, the Blue Screen of Death (BSOD), and viral attacks.
However, when typical boot troubleshooting doesn’t yield results, more advanced techniques like system restores, repair installs, and fresh Windows installations may be necessary. Additionally, hardware diagnostics can identify and address hardware issues. If you’re unsure about advanced troubleshooting, seeking help from a computer expert or the manufacturer’s support is a wise choice. With these strategies, you can tackle complex problems and keep your Windows 10 system running smoothly.