Troubleshooting the computer system, especially in Windows OS devices, can be done from startup. The startup programs in Windows are in the booting process. They are programs that automatically start immediately when the computer boots. While most of them are system software programs, they can also be application software programs. Using the msconfig utility, a Microsoft user may check which programs start when their machine powers up. Via these startup processes, you can control which program starts, or not, especially when aiming to troubleshoot a problem most likely caused by a program.
There are different startup modes on Windows, and the most popular are the normal, and the safe mode. For troubleshooting a computer issue likely caused by startup programs (inbuilt or installed programs) the selective startup could be used. To make use of selective startup in Windows, here is a step-by-step guide on how to do it using the system configuration utility
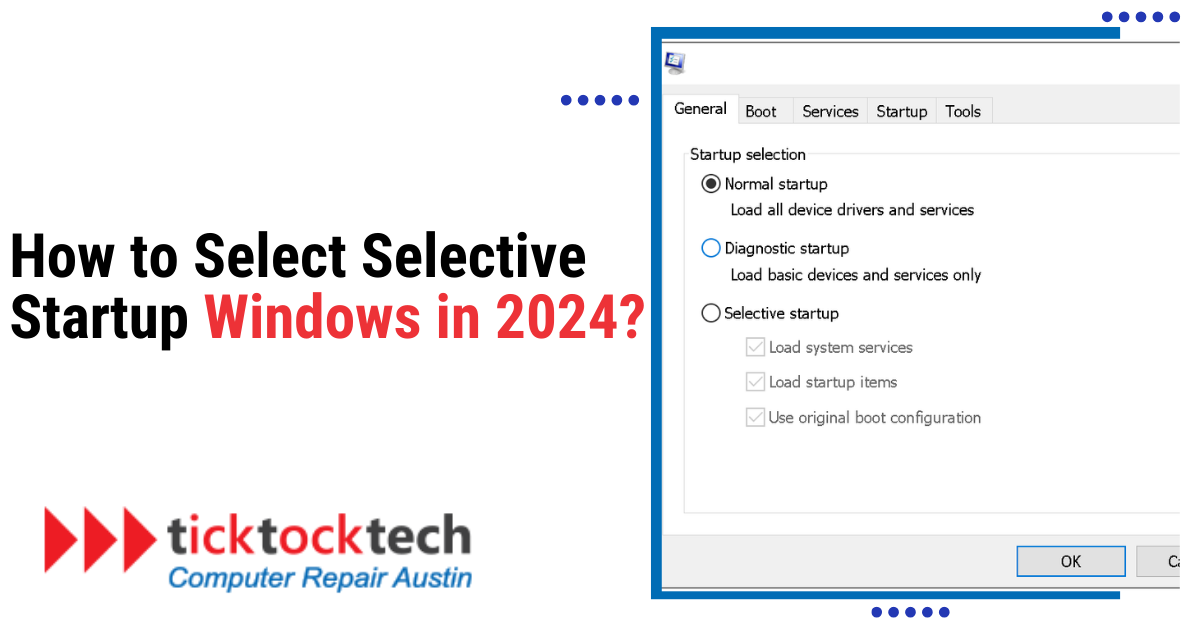
In any Windows version from Windows 8 to 11, you can enable selective startup mode; Press the Windows key and the R key simultaneously. Enter msconfig in the Open field and click OK. Choose Selective Startup from the General tab in the System Configuration window, and then uncheck the Load startup elements tick.
1. Start up your Windows computer
Just like always, turn on your computer. Press the power button and let Windows finish starting up. For now, you don’t need to use any special keys or commands. Just restart your computer and go back to your normal Windows setting.
2. Open System Configurations
To use the System Configuration tool, you must wait until the screen is fully booted up. If you press Windows Key + R, a small run box will appear ready for your order. In the box that comes up, type in msconfig and press Enter. This will open the System Configuration tool, which is where you can change the settings for how the computer starts up.
3. Click on the “General” tab.
There are a few tabs at the top of the System Configuration tool when it first comes up. Click the “General” tab. You can choose what programs to load when Windows starts up from this tab, which is like the control room for how Windows starts up.
4. Choose Selective Startup
There are a few ways to start up your machine under the “General” tab. Find the one that says “Selective startup” and click on it. If you pick this choice, Window will not start any programs that are not on this list. You can pick which system services and startup apps to run when the system starts up with this choice.
In case you missed: Ranking the Most-Watched Super Bowl Halftime Shows
5. Customize Startup
You’ll see that you can be even more exact with your choices when Selective Startup is chosen. This step is all about customization. It lets you change how the computer starts up to fit your wants or your tastes. You can choose between three options: Use of the original boot setup, Load system services, and Load starting items.
Load system services: This is for the important startup services, like the program that sets up the system. This should stay checked so that important system services can start.
Load startup items: If you don’t want startup programs to run immediately, uncheck this box. They can be third-party programs like your protection software, clients for syncing your cloud files, or even smaller utility programs that are meant to make your computer experience better. If you want to fix program problems or use selective starting mode, unchecking this box may help.
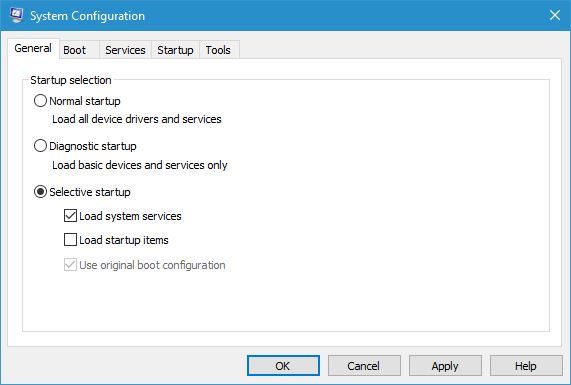
Use the original boot configuration: This is usually left checked to keep the original start options.
6. Manage Startup Programs
Here is where you can start to fine-tune which app starts up when the computer does. In newer versions of Windows, this tab might take you to the Task Manager when you click on it. You can use the “Services” and “Startup” tabs to change even more about which services or apps run at startup:
You can turn on or off individual services on the Services tab. Before making changes, you should make sure that “Hide all Microsoft services” is checked so that you don’t disable any important services by accident.
On the Startup tab (called Task Manager after Windows 8): This tab shows all the apps that run at the start. If you are using Windows 8 or later, clicking on the “Startup” tab will take you to the Task Manager, where you can turn on or off starting programs.
7. Save Changes and Restart the Computer
Now that you’ve chosen everything you want, it’s time to seal the deal. When you’re done making changes, click “Apply” and then “OK” to close the System Configuration. There will be a message that asks you if you want to restart anytime. Go ahead and restart if you’re ready to see what you’ve done. All of the choices you just made will be used when your computer restarts in Selective Startup mode.
How to Change Back from Selective Mode to Normal Startup Mode
When you are done with the purpose of selective mode, you can change back to normal startup same way but in reverse. Here is how to get back to normal startup mode:
System Configuration Tool: Press the Windows key + R, enter msconfig in the run dialog box, and then press Enter. Then go to the “General” page to see your startup settings. Select the “Normal Startup” option to allow Windows to load all drivers and services as it normally does.
Click “Apply,” “OK,” and restart your computer. When you restart your computer, Windows will reverts to its default state, with all services and apps loading as they did before your Selective Startup adventure.
5 Windows Troubleshooting Problems you can solve in Selective Startup Mode
Selective starting mode is a helpful tool for troubleshooting and resolving various Windows issues. Here are five frequent Windows troubleshooting problems you may tackle in selected starting mode: starting Clash, Issues with Windows Services, BIOS or UEFI Issues, Software Conflicts, and Issues with Bootfiles.
1. Troubleshooting Startup Clash.
Startup clash happens when many applications attempt to execute concurrently during the boot process, resulting in conflicts and slowing down the system. Using the selected starting mode, you may detect and deactivate any conflicting apps, allowing your computer to boot up faster and more smoothly.
2. Fixing Issues with Windows Services
Windows services are background processes that operate on your computer and perform a variety of functions. These services may occasionally create conflicts or slowdowns during the boot process. Using the selected starting mode, you may detect and deactivate any troublesome services, allowing your computer to boot up faster and more smoothly.
3. Troubleshooting BIOS/UEFI Issues
BIOS or UEFI errors can lead to a range of difficulties, such as sluggish boot times and boot conflicts. Using the selected starting mode, you may detect and eliminate any troublesome BIOS or UEFI settings, allowing your computer to boot up faster and more smoothly.
4. Troubleshooting Software Conflicts
Software conflicts can cause a wide range of issues, including delayed startup times and crashes during the boot process. Using the selected starting mode, you may detect and deactivate any conflicting applications, allowing your computer to boot up faster and more smoothly.
5. Fixing Problems with Bootfiles
Boot files are files that store the configuration parameters for your computer’s boot process. These files can become damaged or out of date, resulting in conflicts and slowdowns during boot. Using the selected starting mode, you may discover and eliminate any troublesome boot files, enabling your machine to boot up more quickly and smoothly. Repair boot files in 8 steps.
For any further troubleshooting and computer problems, call TickTockTech for a quick check and repair. The good part is the technician comes to you.
FAQs
Selective starting is a troubleshooting mode in Windows OS that allows users to boot up their computer with a minimum collection of drivers and starting apps. This mode aids in the detection and resolution of conflicts or difficulties impacting the system’s performance or stability.
The primary application of Selective Startup on the Windows operating system is to troubleshoot and resolve system issues. Users can diagnose system crashes, slowdowns, and starting difficulties by selectively activating or removing startup items and services.
This will start System Configuration. Press Win + R, type msconfig, and press Enter. Then click the “General” tab, and select “Normal Startup”. When you’re done, click “OK.” You will need to restart your computer for the changes to take place.