Windows system error codes are cryptic messages that appear when something goes wrong with your computer. Understanding these codes is crucial for troubleshooting issues much faster and maintaining your system’s health.
What are System Error Codes?
System Error Codes are alphanumeric values assigned by Windows Operating System to signify specific issues or problems that occur within the system.
Windows system error codes are like secret messages from your computer. When something goes wrong, these codes pop up to help you figure out what the problem is. They’re like clues in a detective story, leading you to the source of the issue.
In addition, system error codes usually show up as a message box or a dialog box on your screen. They’ll have a number and sometimes a short description of the problem.
Related: Why does my computer screen keep going black?
Causes of Windows System Error Codes
Windows System Error Codes can stem from different causes. Understanding the root cause is crucial for effectively troubleshooting and resolving these errors.
Some common causes of system error codes include:
- Corrupted system files. This occurs through unexpected shutdowns, software crashes, or malware.
- Hardware conflicts. When multiple devices try to use the same resource, it confuses your operating system.
- Outdated or faulty drivers.
Common Windows System Error Codes and How to Fix Them
1. Windows Update Error 0x80070057
Windows Update Error 0x80070057 is a common issue that can occur when attempting to install updates for your Windows operating system.
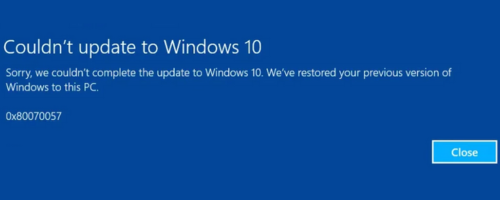
Some of the common reasons for this error include:
- Corrupted Windows Update Files
- Incorrect System Date and Time
- Antivirus or Firewall Interference
- Insufficient Disk Space
- Pending System Restarts
How to Fix Error 0x80070057
To resolve Windows Update Error 0x80070057, try the following steps:
1. Check Date and Time Settings:
- Right-click the clock on your taskbar and select “Adjust date/time.”
- Ensure that the date, time, and time zone are correct.
- Click “Sync now” to synchronize your computer’s clock with an internet time server.
2. Disable Antivirus and Firewall Temporarily:
- Right-click the antivirus icon in the taskbar and select “Disable” or “Turn Off.”
- Open your firewall settings and temporarily disable it.
3. Clear Temporary Update Files:
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type “temp” and press Enter.
- Select all files and folders in the Temp folder and delete them.
4. Run the Windows Update Troubleshooter:
- Press Windows Key + I to open the Settings app.
- Go to “Update & Security” > “Troubleshoot.”
- Click on “Additional troubleshooters” and select “Windows Update.”
- Run the troubleshooter and follow the on-screen instructions.
5. Reset Windows Update Components:
- Open an elevated Command Prompt (Run as administrator).
- Type the following commands one by one and press Enter after each command:
net stop wuauserv
net stop cryptSvc
net stop bits
ren C:\Windows\SoftwareDistribution SoftwareDistribution.old
ren C:\Windows\System32\catroot2 Catroot2.old
net start wuauserv
net start cryptSvc
net start bits6. Perform a System Restore:
- If the error persists, perform a System Restore to the point before the error.
2. Blue Screen Stop Errors
Blue screen stop errors, also known as Blue Screens of Death (BSODs), is a critical system error that can make your Windows computer suddenly crash. This error indicates a serious problem that requires immediate attention to prevent data loss or hardware damage.
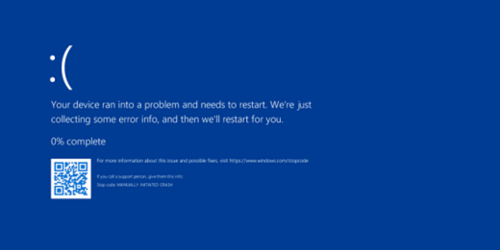
Blue screen errors can be caused by issues like:
- Faulty Hardware
- Outdated or Corrupted Drivers
- Software Incompatibility
- Malware Infections
- Overclocking
Common Blue Screen Error Codes
Some common blue screen error codes include:
- DRIVER_IRQL_NOT_LESS_OR_EQUAL: This error indicates a problem with a device driver.
- PAGE_FAULT_IN_NONPAGED_AREA: This error occurs when the operating system tries to access a part of memory that is not available.
- NTFS_FILE_SYSTEM: This error indicates a problem with the file system on your hard drive.
- DATA_BUS_ERROR: This error occurs when there’s a problem with the communication between your computer’s memory and other components.
- MACHINE_CHECK_EXCEPTION: This error indicates a hardware problem, such as a faulty CPU or memory.
- INACCESSIBLE_BOOT_DEVICE: This error occurs when the operating system cannot access the boot device, such as your hard drive.
- HAL_INITIALIZATION_FAILED: This error indicates a problem with the hardware abstraction layer (HAL), which is responsible for communication between the operating system and hardware.
- WHEA_UNCORRECTABLE_ERROR: This error indicates a hardware problem that cannot be corrected by the operating system.
How to Fix Blue Screen Stop Errors
If you encounter a blue screen error, follow these steps to troubleshoot the issue:
1. Restart Your Computer:
- Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve the error.
2. Check Hardware Connections:
- Ensure that all cables and connections are secure, especially for components like RAM and storage devices.
3. Update Drivers:
- Keep your device drivers up-to-date to avoid compatibility issues.
4. Scan for Malware:
- Run a full system scan with a reputable antivirus program to rule out malware infections.
5. Repair System Files:
- Use the System File Checker (SFC) tool to scan and repair corrupted system files. Open an elevated Command Prompt and type “sfc /scannow.”
6. Check Hard Drive Health:
- Use the Check Disk (CHKDSK) tool to scan your hard drive for errors. Open an elevated Command Prompt and type “chkdsk /r.”
7. Reset Windows:
- If the error persists, consider resetting Windows to reinstall the operating system while preserving your personal files.
Related: How to Fix “Missing Operating System” on Your Computer
3. DLL Errors
DLL (Dynamic Link Library) errors occur when a program tries to access a DLL file that is missing or corrupted. These DLL files are shared libraries that contain code and data used by multiple programs on your computer. When a program cannot find or use the DLL file it needs, it can result in an error message and the program may not function properly.
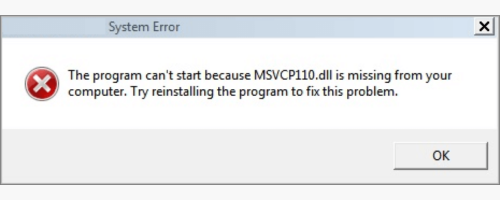
There are several reasons why DLL errors may occur:
- Missing DLL Files
- Corrupted DLL Files
- Version Conflicts
- Incompatible Software
How to Fix DLL Errors
To resolve DLL errors, try the following:
1. Restart Your Computer:
- Sometimes, a simple restart can resolve DLL errors by refreshing the system and clearing temporary issues.
2. Check the Recycle Bin:
- If you recently deleted a DLL file, check the Recycle Bin and restore it.
3. Scan for Malware:
- Run a full system scan with an updated antivirus program to detect and remove any malware that may have corrupted DLL files.
4. Reinstall the Program:
- If the DLL error is related to a specific program, try reinstalling that program. This can replace any missing or corrupted DLL files.
5. Update Drivers:
- Outdated drivers can cause DLL errors. Check for updates for your device drivers and install any available updates.
6. Use System Restore:
- If the DLL error started occurring after a recent change to your system, such as installing a new program or updating Windows, you can try performing a System Restore to revert your system to an earlier point.
7. Manually Register DLL Files:
- In some cases, you may need to manually register DLL files. To do this, open an elevated Command Prompt (Run as administrator) and type the following command:
regsvr32 <path_to_dll_file>- Replace “<path_to_dll_file>” with the full path to the DLL file.
8. Download DLL Files:
- As a last resort, you can try downloading the missing DLL file from a reputable source and placing it in the appropriate system folder. However, be cautious when downloading DLL files from third-party websites, as they may contain malware.
4. Access Denied Folder Errors
Access denied folder errors occur when you try to access a folder on your PC but you’re denied permission.
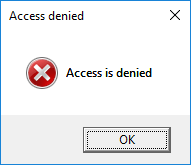
You may encounter access denied folder errors because:
- Insufficient Permissions
- File System Errors
- Malware Infections
How to Fix Access Denied Folder Errors
To resolve access denied folder errors, follow these steps:
1. Check Folder Permissions:
- Right-click on the folder and select “Properties.”
- Go to the “Security” tab and click on the “Advanced” button.
- In the “Advanced Security Settings” window, check the “Owner” section to see who owns the folder.
- If you are not the owner, you can try to change the ownership of the folder by clicking on the “Change” button.
- In the “Permissions” tab, check the permissions for your user account or group. Make sure that you have the “Read” and “Write” permissions.
2. Repair File System Errors:
- Open a Command Prompt window (press Windows Key + R, type “cmd”, and press Enter).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
chkdsk /r- This command will scan your hard drive for errors and attempt to repair them.
3. Scan for Malware:
- Run a full system scan with an updated antivirus program to detect and remove any malware that may be causing the access denied errors.
4. Take Ownership of the Folder (Advanced):
- If you are unable to change the ownership of the folder through the Properties window, you can try taking ownership of the folder using the Command Prompt.
- Open a Command Prompt window (press Windows Key + R, type “cmd”, and press Enter).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
takeown /f <folder_path> /r5. Reset Folder Permissions (Advanced):
- If taking ownership of the folder doesn’t work, you can try resetting the folder permissions using the Command Prompt.
- Open a Command Prompt window (press Windows Key + R, type “cmd”, and press Enter).
- Type the following command and press Enter:
icacls <folder_path> /reset5. POST Beeps
POST (Power-On Self-Test) beeps are a series of short beeps or tones you experience during PC startup. These beeps indicate the status of the POST process, which checks the hardware components of your computer to ensure they are functioning perfectly. Different beep codes correspond to different hardware issues.
These beep codes vary depending on the manufacturer and model of your computer. However, here are the most common POST beep codes and their meanings:
- Single Beep: This usually indicates that the POST process is successful and the computer is ready to boot.
- Two Beeps: This often indicates a problem with the motherboard.
- Three Beeps: This usually indicates a problem with the memory (RAM).
- Four Beeps: This often indicates a problem with the graphics card.
- Five Beeps: This usually indicates a problem with the CPU.
- Six Beeps: This often indicates a problem with the keyboard controller.
- Seven Beeps: This usually indicates a problem with the hard drive.
- Eight Beeps: This often indicates a problem with the CMOS (Complementary Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor) chip, which stores the BIOS settings.
- Continuous Beeping: This usually indicates a severe hardware failure that prevents the computer from booting.
Troubleshooting POST Beep Codes
When you hear a POST beep code, it’s important to identify the specific code and then troubleshoot the corresponding hardware component. Here are some general steps you can take:
1. Check Connections:
- Make sure all cables and connections are secure, especially for components like the CPU, memory, graphics card, and storage devices.
2. Reseat Components:
- Try reseating the hardware components, such as the memory modules and graphics card, to ensure proper contact.
3. Update BIOS:
- Check if there’s a BIOS update available for your motherboard. Updating the BIOS can sometimes resolve POST beep code issues.
4. Test Components:
- Test the suspected faulty component on another computer to confirm the issue.
Frequently Asked Questions on Windows System Error Codes
Windows error codes are cryptic messages that appear when something goes wrong with your computer. They help you identify and troubleshoot specific issues in your computer.
Windows errors can be caused by factors like corrupted system files, hardware conflicts, outdated or faulty drivers, malware infections, insufficient disk space, and pending system restarts.
Conclusion: Windows System Error Codes in 2024
Windows system error codes provide valuable information about PC problems. Understanding the causes of these errors and implementing preventive measures will help maintain a healthy and efficient Windows system. Regular system maintenance, software updates, and security measures reduce the occurrence of Windows errors. If you encounter persistent errors, consult a reliable computer repair company to identify and troubleshoot the problem.

