If you’ve been around the tech block, you’ve probably heard the term “mesh network” thrown about. In this article, we will explain the concept of a mesh network, discuss its benefits and applications, and explore whether it is a superior alternative to traditional WiFi networks.
What is a Mesh Network?
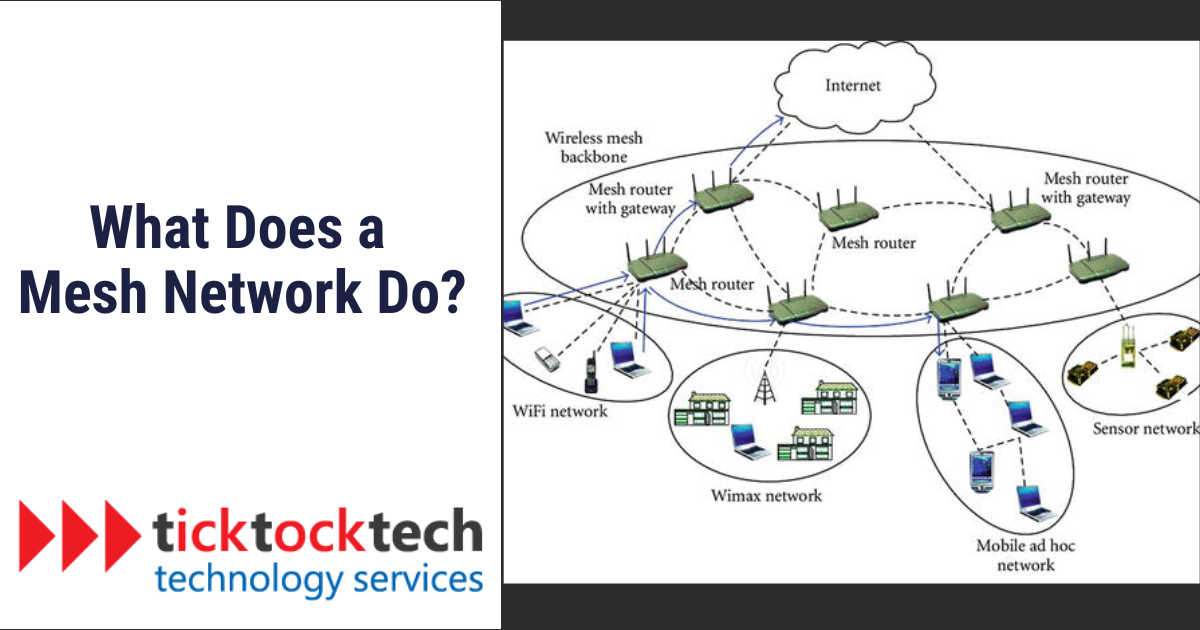
A mesh network is a type of network architecture where devices, known as nodes, are interconnected in a web-like pattern. Unlike traditional networks that rely on a central router as the main hub, a mesh network establishes a network of nodes that work together to ensure efficient data routing and a reliable connection.
The beauty of a mesh network lies in its ability to create multiple pathways for data transmission. Imagine a network where devices branch off from each other, forming a mesh of interconnected nodes. This unique topology enables the network to efficiently route data between devices for a seamless and robust connection.
One of the key advantages of a mesh network is its capacity to provide consistent connectivity in a space. By strategically placing nodes in an area, mesh networks eliminate frustrating dead zones where the signal strength drops or disappears entirely. If you’re in a large home, an office building, or a sprawling outdoor environment, a mesh network ensures that you stay connected without interruptions.
To make the network more robust, mesh networks create multiple pathways for data to travel between connected devices. This ensures that if one device or connection stops working, the information can automatically find another route to reach its destination. It’s like having a backup plan in place that kicks in whenever there’s a network problem.
In larger deployments, mesh networks can include multiple routers, switches, and other devices that operate as nodes. This scalability allows the network to span a vast area, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Whether you’re setting up a network for a small office or deploying a wireless infrastructure for a large campus, a mesh network is a reliable option.
Why would you use a Mesh Network?
So, why would you use a mesh network? Whether you’re a homeowner seeking consistent coverage in your space or a business owner wanting to ensure uninterrupted productivity, a mesh network is the answer. Here are some of the top benefits of a mesh network.
- Extensive Coverage: One of the main advantages of a mesh network is its ability to provide extensive coverage. Unlike traditional Wi-Fi extenders, which create new access points, a mesh network works by repeating the signal from the previous device. This means that each device in the network acts as a relay, ensuring that the Wi-Fi signal reaches every corner of your home.
- Easy Setup: Setting up a mesh network is relatively easy. All you need to do is connect the primary node to your existing modem or router, and then place the additional nodes throughout your home. These nodes communicate with each other wirelessly for a reliable network without any complicated configuration.
- Flexibility: Mesh networks offer great flexibility, making them suitable for homes of all sizes. Whether you have a small apartment or a large house, a mesh network can adapt to your needs. You can add more nodes to expand the coverage area or remove nodes if you don’t need as much coverage. It’s a scalable solution that grows with you.
- Reliability: Unlike traditional routers, where a single point of failure can bring down the entire network, mesh networks are resilient. Each node in the network is connected to a power source, ensuring that even if one node fails, the rest of the network can continue functioning.
Types of Mesh Networks
There are different types of mesh networks, each with its unique characteristics and advantages.
1. WiFi Mesh Networks
WiFi mesh networks are the most common type of mesh network. They are wireless networks that use radio waves to communicate between nodes. These networks are often used in homes, offices, and public hotspots to provide internet access. WiFi mesh networks are easy to set up and do not require any wiring between nodes. They are also cost-effective and can provide coverage over a large area.
2. Wired Mesh Networks
Wired mesh networks, on the other hand, use Ethernet cables to connect nodes. They are often used in industrial settings where a wired connection is more reliable. Wired mesh networks are more expensive to set up than WiFi networks, but they offer faster data transfer rates and are more secure.
3. Full Mesh Topology Networks
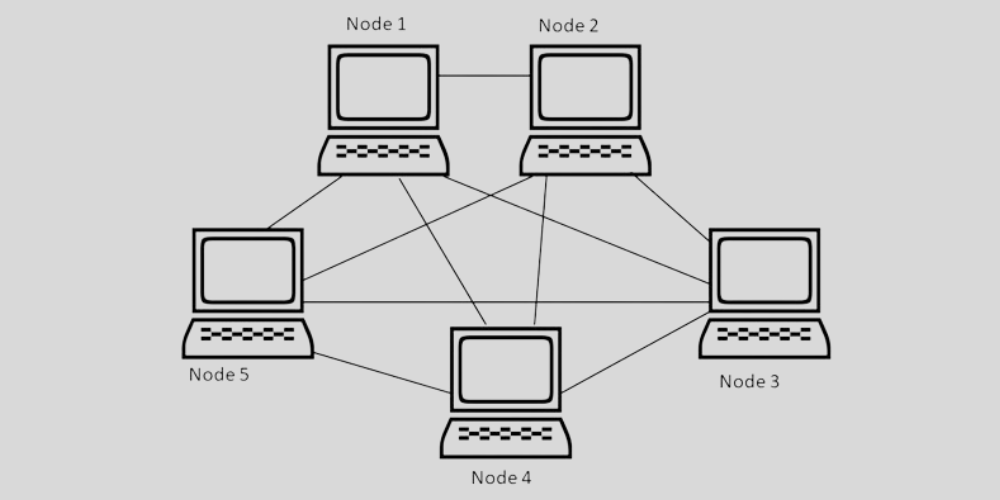
A full mesh topology network is a network where each node is connected to every other node. This type of network is often used in critical infrastructure, such as power grids and transportation systems, where redundancy and reliability are crucial. Full mesh topology networks are expensive to set up and maintain, but they offer the highest level of redundancy and can withstand multiple node failures.
4. Partial Mesh Topology Networks
A partial mesh topology network is a network where only some nodes are connected to every other node. This type of network is often used in scenarios where not all nodes need to communicate with each other. Partial mesh topology networks are more cost-effective than full mesh networks but still offer a high level of redundancy.
Related: How To Check If Someone Is Remotely Accessing Your Computer
5. Hybrid Mesh Networks
Hybrid mesh networks combine both wireless and wired networks to create a robust and reliable communication system. These networks use a wired interface to cover a larger area and a wireless interface to connect devices. Hybrid mesh networks are often used in smart cities and IoT applications where both wired and wireless connectivity are necessary.
6. Infrastructure Mesh Architecture Networks
Infrastructure mesh architecture networks use a combination of mesh and star topologies to create a highly efficient and reliable network. These networks are often used in large-scale enterprise environments where high-performance computing and low latency are essential. Infrastructure mesh architecture networks are expensive to set up but offer a high level of scalability and reliability.
7. Client-Based Mesh Architecture Networks
Client-based mesh architecture networks connect client nodes peer-to-peer. Each node acts as a mesh router and can send data packets to other nodes. These networks are often used in scenarios where a centralized server is not necessary or desirable. Client-based mesh architecture networks are easy to set up and offer a high level of decentralization.
Application of Mesh Network
Mesh networks have revolutionized the way we communicate and interact with our surroundings. From home automation to industrial monitoring, military communications, and medical monitoring, mesh networks have proven to be a versatile and reliable technology. Here are some of the key applications of mesh networks:
- Home Management: Mesh networks have simplified home automation. Mesh networks make this possible, allowing you to turn lights off and on, dim them, or even change their color with ease.
- Building Management: Mesh networks aren’t just for homes. Large office buildings and other structures also benefit from the energy savings that mesh networks provide.
- Industrial Monitoring: Mesh networks play a crucial role in industrial settings. They serve as a reliable feedback link in control systems for condition monitoring and predictive maintenance.
- Military Communications: Mesh networks play a critical role in military communications. Mesh networks provide a seamless way for military personnel to communicate and share information, even in the most challenging environments.
- Medical Monitoring: Medical professionals use mesh networks to monitor patients’ vital signs, track their movements, and receive alerts during emergencies.
- Consumer Electronics: Specialized mesh networks provide an easy way to connect home entertainment systems by eliminating the need for tangled wires and complicated setup processes.
- Broadband Wireless Access: In addition, mesh networks are used to provide high-speed Internet connections and other broadband services in areas where cable TV or DSL lines aren’t available.
Is a Mesh Network better than WiFi?
Both mesh network and traditional WiFi have their strengths and weaknesses, and the right choice depends on factors like the size of the space, the number of devices connecting, and your budget.
Traditional WiFi is a centralized system where a single router acts as the central access point for all devices. This means that all traffic is funneled through this one point, which can lead to congestion or slower speeds in larger spaces or with many devices.
On the other hand, a mesh network is a decentralized system where multiple access points work together to provide coverage across a larger area. This means that devices can connect to the nearest access point, rather than relying on a single central point. This provides faster and more reliable connections in areas with physical barriers.
So, is a mesh network better than WiFi? It depends on your specific needs. If you have a smaller space and a lower number of devices, traditional WiFi may be sufficient. However, if you have a larger space or are dealing with a high number of devices, a mesh network is a better choice.
Frequently Asked Questions
A mesh network is a great choice to ensure consistent WiFi coverage. Mesh networks are flexible, easy to set up, and can be scaled to fit your needs. They are particularly beneficial for larger spaces or areas with physical barriers that interfere with WiFi signals.
It depends on your specific needs. Mesh networks are better in larger spaces with many devices, while traditional WiFi may be sufficient for smaller spaces and fewer devices.
While mesh networks offer many benefits, there are a few potential disadvantages to consider. One disadvantage is the cost. Additionally, the performance of a mesh network may be affected by the distance between nodes. If the nodes are too far apart, the signal strength may decrease. However, this can be fixed by strategically placing nodes throughout the space.
Conclusion
Mesh networks are an efficient way to provide extensive network coverage in a large space. They offer several benefits, including easy setup, flexibility, and scalability, making them suitable across many industries. Their ease of setup and robust performance make them a compelling choice for anyone seeking seamless connectivity across large spaces.