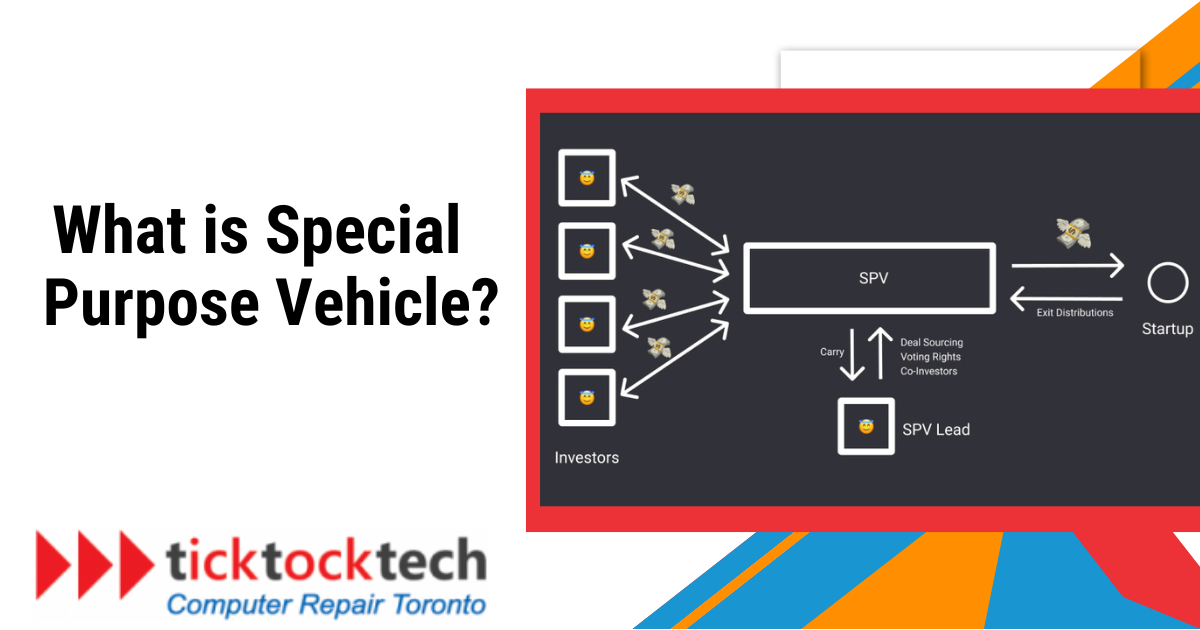
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is an essential component of both strategic investments and intricate financial operations. Let’s examine the contents of the SPV and its function in the financial industry.
What is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)?
A legal entity established to achieve a particular, restricted goal is known as a special purpose vehicle (SPV). It is a kind of organizational structure that helps businesses accomplish their objectives more successfully by separating financial risk. Although they are often employed in financial transactions, special-purpose vehicles (SPVs) are also used in many other industries.
Related: What to look for in finance internships? 2024 Updated.
How Does an SPV Work?
Generally speaking, an SPV is a subsidiary business that exists independently of its parent firm and has its assets and liabilities. Because of this division, the parent firm can take part in deals or operations that could be too dangerous for the primary business. The balance sheet of the parent company is not directly impacted by SPV’s debt, investments, or other financial operations.
They are frequently employed to combine funds from several investors for a certain business endeavor or project. Because the SPV is responsible for the venture’s finances, this structure protects investors from some risks and liabilities. Profits are distributed in an orderly and transparent manner to investors utilizing the Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) when they are made.
What are the Uses of special-purpose vehicle SPV?
- Risk Sharing: Through the use of Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs), businesses can share project risks with investors, safeguarding their interests and encouraging cooperation while reducing possible losses.
- Angel Investors: Angel investors can pool resources, diversify portfolios, and engage in high-value investments with peers by using Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) to gain access to larger deals.
- Securitization: SPVs separate loans from other liabilities by securitizing them, giving investors access to structured assets and improving market liquidity.
- Venture Capitalists: Venture capitalists employ special purpose entities (SPVs) as means of co-investment, which facilitates the effective allocation of capital across various firms and offers adaptability in fundraising tactics.
- Asset Transfer: SPVs provide a practical means of transferring ownership without interfering with business activities, streamlining the asset transfer procedures involved in mergers and acquisitions.
- Corporate Entities: SPVs let corporate entities pursue strategic initiatives by enabling them to segregate assets, efficiently manage risks, and investigate novel business opportunities without compromising their primary business operations.
- Property Sales: Businesses use Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) to structure transactions in a way that minimizes tax obligations and maximizes profits.
Related: How to start a career in Finance With No Experience
Types of special-purpose vehicle
Fund managers have two main options to choose from when creating an SPV: Limited Liability Company (LLC) or Limited Partnership (LP).
LLC Special Purpose Vehicle
In the US, venture capital firms frequently use LLC SPVs. The LLC, which was established only for investment purposes, is membership-based. A manager is subsequently appointed by the LLC to supervise daily activities. Even though LLC SPVs are permitted to conduct business abroad, they could have trouble accepting foreign investment.
LP Special Vehicle
LP SPVs have extra advantages over LLCs, especially when dealing with foreign entities, but they nevertheless provide comparable protections and benefits. Globally recognized, LP SPVs are especially appropriate for fund managers looking to raise money from foreign investors.
See Also: Top 7 Highest Paying Jobs in Finance 2024
Pros and Cons of Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV)
Pros of special purpose vehicles (SPVs)
- Improved Financing Opportunities: By securing better financing terms in SPVs, lenders are drawn in by the isolation of financial risk.
- Optimized Capital Impact: Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) focus capital on certain endeavors, guaranteeing increased profits and significant project participation.
- Target Your Network: Because SPVs are simpler to set up than investment funds, they make it easier for networks to share deals.
- Operational Effectiveness: By separating assets or projects, SPVs simplify operations and cut down on complexity and overhead.
- Targets Are Easier to Reach: By making participation more accessible, pooling money makes it easier to achieve minimum investment criteria.
- Assisted Fundraising: A larger pool of possible investors is reached because SPVs frequently have lower minimum investment criteria.
- Clear Cap Table: Reduces management time and costs by streamlining target firm cap tables.
Cons of special purpose vehicles SPVs (SPVs)
- Professional Management Requirement: The management of SPVs must be specialized, which complicates operational control.
- Brand Risks: Despite formal separation, issues within an SPV have the potential to damage the parent company’s brand.
- Regulatory and compliance risks: Special purpose entities (SPVs) are required to abide by certain regulations; failure to do so may result in legal and/or financial ramifications.
- Costs and Fees: There are extra costs associated with creating and managing SPVs, such as accounting, legal, and management fees.
- Financial risk: SPVs are linked to a higher financial risk, particularly for projects that have a significant risk of failure.
See Also: What Roles Fit in for a Business Systems Analyst?
Take Away
A Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) is a legal entity that is separate from its parent company and is used to achieve specific goals or manage financial operations. SPVs are commonly used in various industries, including finance, to share risks, attract investors, securitize assets, and facilitate strategic initiatives. There are different types of SPVs, such as LLCs and LPs, each with its advantages and considerations. While SPVs offer benefits such as improved financing opportunities and operational effectiveness. They also come with challenges such as the need for specialized management and potential regulatory risks. Overall, SPVs provide a practical and efficient way for businesses to achieve their objectives while mitigating risks and maximizing profits.